- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Fuel Cells
Fuel cells directly generate electricity as a result of the electrochemical reaction of hydrogen and oxygen. This system is the opposite of electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen and oxygen. In fuel cells, hydrogen is used as fuel, and only water is released as a result of the reaction. Therefore, fuel cells are an environmentally friendly and highly efficient energy production technology.
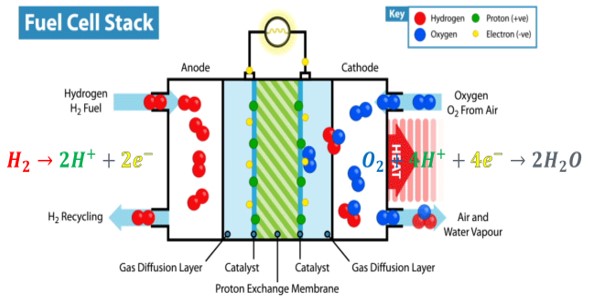
A fuel cell is basically made up of three main components
- Anode (negative electrode): Hydrogen is oxidized here and broken down into protons and electrons.
- Cathode (positive electrode): Oxygen combines with electrons here to form water.
- Electrolyte: It allows protons to move between the anode and cathode.
The electrons resulting from this process move in the external circuit and produce electrical energy. Fuel cells can run non-stop when hydrogen is continuously supplied.
- Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC): Operates at medium temperature, suitable for large-scale power generation.
- Alkaline Fuel Cell (AFC): Used in spacecraft, it is highly efficient.
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC): Operates at medium temperature, suitable for large-scale power generation
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC): It works at high temperature, it is preferred in industrial applications.
- Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell (MCFC): It is used in power plants that require high temperatures
- Direct Methanol Fuel Cell (DMFC): Uses liquid methanol, suitable for portable electronic devices
- Zinc Air Fuel Cell (ZAFC): It is used in lightweight and portable energy solutions
- Proton Ceramic Fuel Cell (PCFC): It works efficiently at high temperatures
Fuel cells have a wide range of uses, from electric vehicles to portable power systems to large power plants.