- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen is not found in pure form in nature, so energy must be used to obtain it. The energy sources used in hydrogen production can be fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas), nuclear energy, and renewable energy sources (solar, wind, biomass, water, geothermal, wave and tidal energy). Using these sources, hydrogen production is carried out by different methods.
Chemical, thermochemical and electrochemical methods are used to produce hydrogen. Today, the most widely used methods are techniques that enable hydrogen to be obtained from fossil fuels. However, renewable energy-supported methods that do not harm the environment are also gaining more and more attention.
1. Oxidation Oxide (POX)
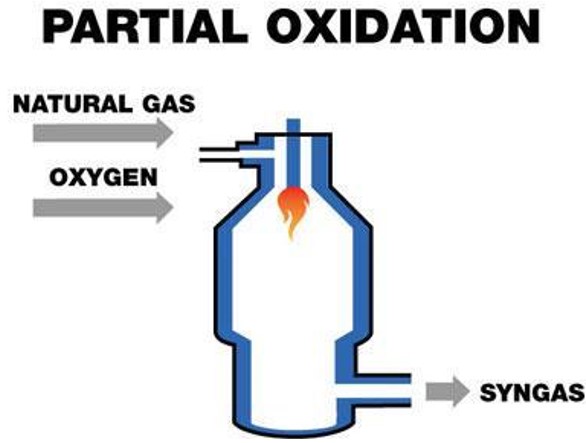
In this method, hydrocarbons (e.g., natural gas) react with small amounts of oxygen to form hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other gases. The process takes place at very high temperatures and usually does not require a catalyst. Some of the gases produced are burned during the process, ensuring the continuity of the system.
2. Auto-Thermal Reforming (ATR)
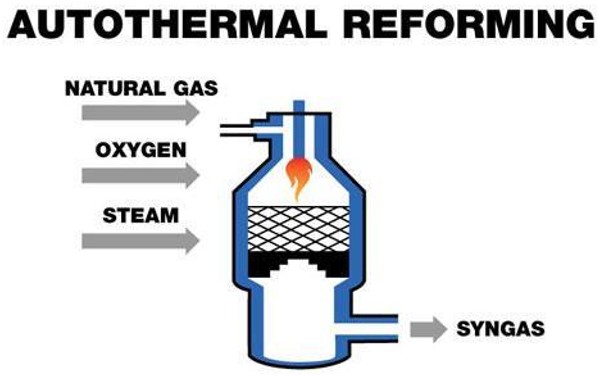
This method produces hydrogen by combining both heat-requiring (endothermic) and heat-releasing (exothermic) reactions. It creates a more efficient production process by allowing the environment to heat up spontaneously. ATR is one of the methods that provides high yields in hydrogen production.
3. Gasification
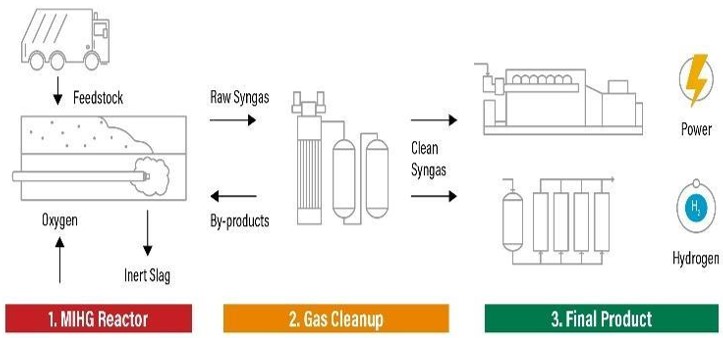
Gasification produces hydrogen by processing substances such as coal or biomass under high temperature and pressure. During this process, gases such as hydrogen, carbon monoxide and methane are released. If biomass is used, it is important to remove moisture to increase yields.
4. Pyrolysis
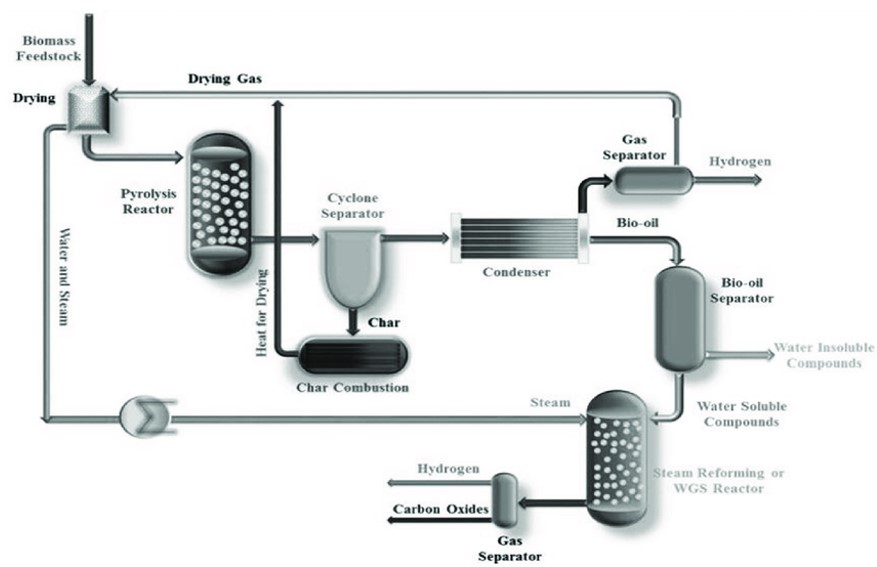
Pyrolysis allows hydrogen to be obtained by breaking down organic substances by exposing them to high temperatures in an oxygen-free and waterless environment. It is generally used for the purpose of evaluating organic wastes and takes place at low temperatures.
5. Electrolysis
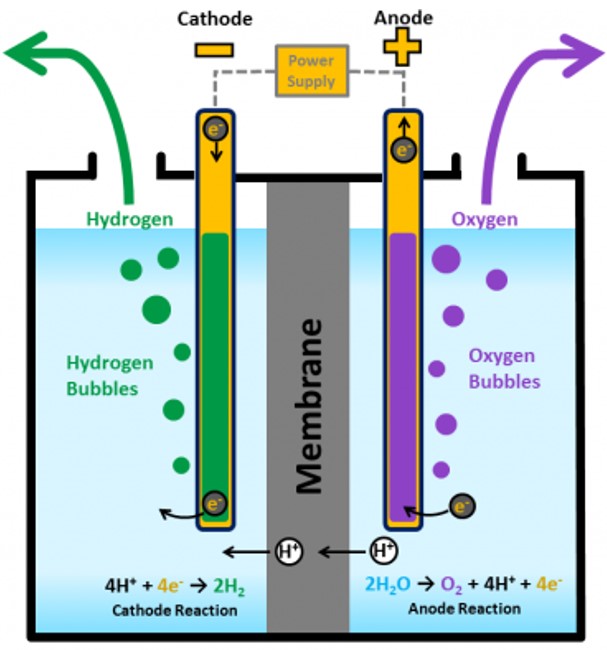
Electrolysis is the process of splitting water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen using electric current. This method becomes an environmentally friendly and sustainable method of hydrogen production, especially when combined with renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. Hydrogen produced by electrolysis is a clean and carbon-free energy source.