- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Bioethanol Technology
Bioethanol is a fuel of biological origin that was developed due to the depletion of fossil fuels and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It is the most widely used biofuel in the world and is used as an alternative motor fuel, especially mixed with gasoline.
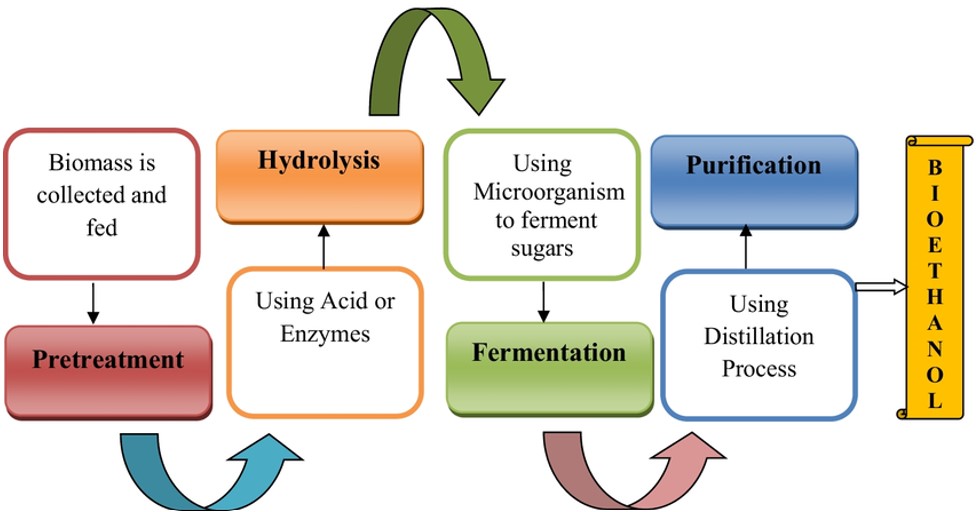
Ethanol is a compound formed as a result of the fermentation of sugars by yeasts. Cereals, sugar crops, and starch-containing plants are the most common sources of bioethanol production. In addition, cellulosic materials such as trees, grasses and household waste can also be used to obtain bioethanol. However, the production of bioethanol from cellulosic materials is more complex and costly compared to the production directly from agricultural products containing sugars and starches. Therefore, technological advances are needed for more efficient production methods.
In order to prevent this problem, alternative sources should be used in bioethanol production instead of agricultural products with food value. These include lignocellulosic plants with no food value and agricultural residues (unused parts such as stems, roots). Thus, both energy needs can be met and food safety is protected.
Products such as corn, sugar beet and sugar cane, which are used for the production of bioethanol, are also staple food sources. For example, in the U.S., a large portion of corn production is used for bioethanol. This leads to an increase in corn prices around the world and competition between food production and energy production.