- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Domestic PV Systems
Domestic photovoltaic (PV) systems are systems that meet the energy needs of homes by converting sunlight into electrical energy. Excess electricity produced by solar panels can be transferred to the city grid and energy can be taken from the grid when needed.
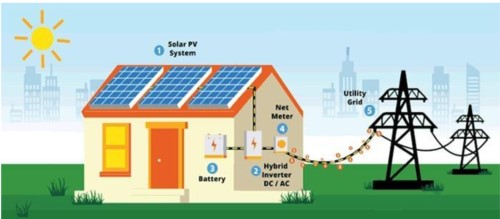
Features:
- There is no need for energy storage, because excess energy is sent directly to the grid.
- DC electricity produced by the panels is converted to AC by inverters and becomes usable at home.
- Power capacity can vary between 1 kW and 50 kW.
- Dual meters are used: One measures the electricity drawn from the grid, the other measures the electricity given to the grid.
- Electronic control devices provide safety by shutting down the system in the event of a possible fault.
Components of domestic PV systems
Solar panels: Provides energy production according to need.
Inverter: Converts DC electricity to AC electricity used in the home.
Electronic control devices: Ensures system safety and stops the system in case of malfunctions.
Meters: Monitors energy production and consumption.