- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Solar Energy Conversions
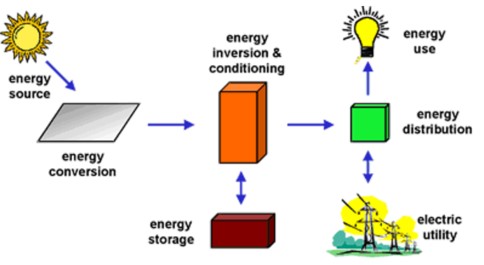
A portion of the energy emitted by the Sun is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, while another portion is reflected back into space. Approximately 50% of this energy is absorbed by the Earth's surface and utilized in various processes. Solar energy can be converted into different forms of energy, either through naturally occurring processes or through methods developed by humans.
Natural Conversions
Solar energy enables numerous natural processes, either directly or indirectly:
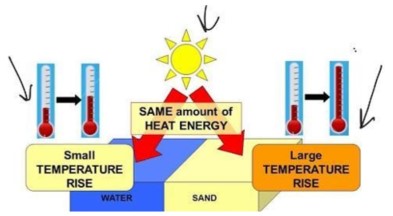
- Heating of Soil and Water: Solar radiation heats the soil and water, influencing air temperature and climate conditions.
- Photosynthesis Process: Plants utilize sunlight to produce food and release oxygen.
- Water Cycle: Solar heat drives the evaporation of water, leading to cloud formation and precipitation, sustaining the water cycle.
- Wind and Wave Formation: Temperature differences in the atmosphere generate winds, which in turn contribute to wave movement.Water Cycle: Solar heat drives the evaporation of water, leading to cloud formation and precipitation, sustaining the
- Natural Wildfires: During dry periods, intense sunlight can trigger forest fires.
Artificial Conversions
Humans can utilize solar energy directly or indirectly through various technologies:

- Solar Collectors: These devices capture solar radiation and use it for heating water or other heating systems.
- Photovoltaic (PV) Panels: These panels convert solar energy directly into electricity.
- Hydraulic Energy: Solar energy drives the water cycle, contributing to electricity generation from dams.
- Wind Turbines: Wind energy, created by temperature differences caused by the Sun, is harnessed to produce electricity.
- Biomass Energy: Plants store solar energy and are used for biofuel production.
- Solar Architecture: This involves designing buildings to maximize the efficient use of solar energy.
These various conversion processes of solar energy not only help maintain ecosystem balance in nature but also provide sustainable energy sources for human use.