- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
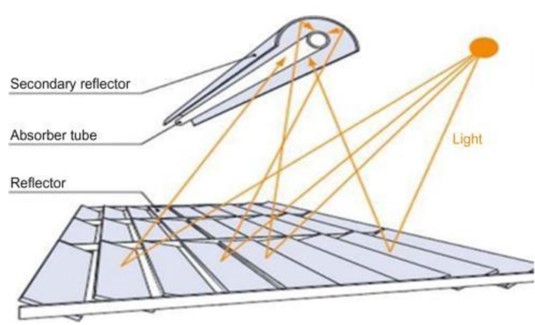
Lineer Concentrators
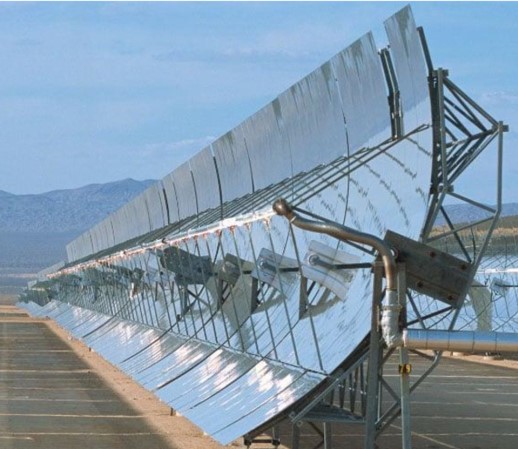
Parabolic Trough Collectors
Parabolic trough collectors are systems that reach high temperatures by concentrating the sun's rays along a line. The inner surface of the collectors is covered with a reflective material and directs the rays to a pipe located at the focal point. Oil is usually used as a heat transfer fluid in the pipe. This fluid heats up to 350-400°C and is used for electricity generation in power plants. Efficiency is increased thanks to the mobile systems that follow the sun's rays.

Fresnel Mirror Condensers
Fresnel mirror concentrators are a system that concentrates linear solar radiation to achieve high temperatures. They operate similarly to parabolic trough collectors, but use many small, movable mirrors with a flatter surface. These mirrors track the sun on a single axis and direct the rays to the collector at the top. They are seen as an economical alternative due to their low production costs. They are used in Nevada Solar One, California SEGS Plant and various plants in Spain.