- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
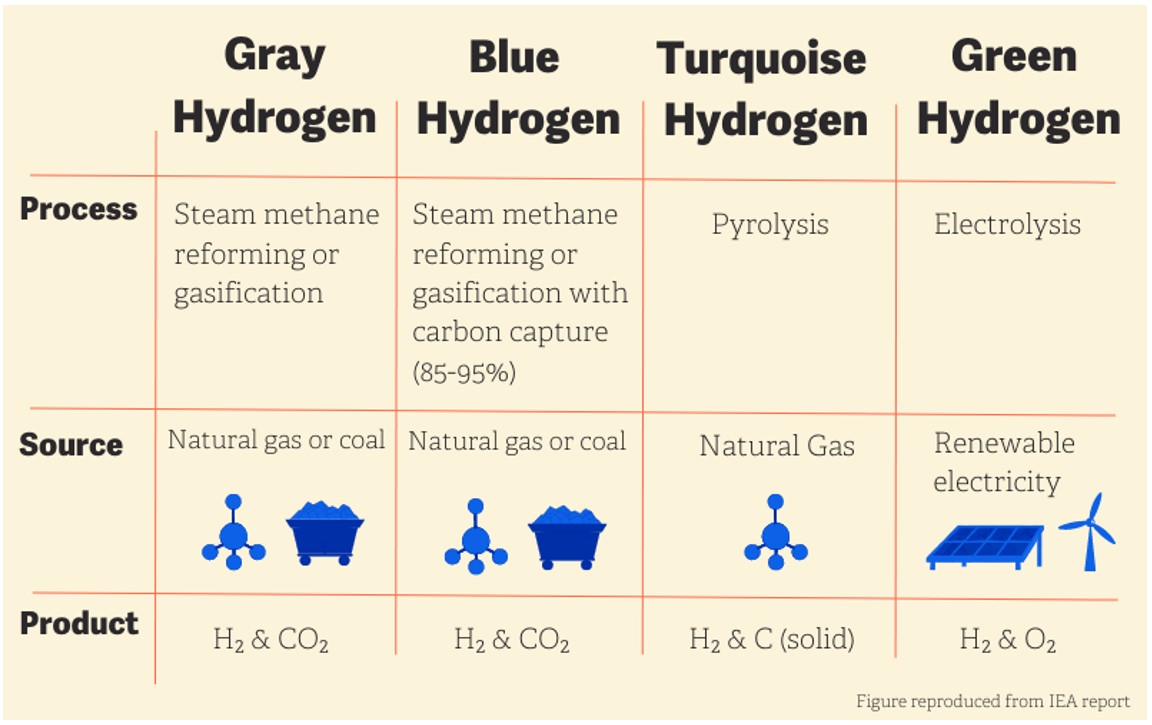
Green Hydrogen
Green hydrogen is a type of hydrogen that is produced with renewable energy sources without harming the environment. This is much more environmentally friendly compared to fossil fuels, as there are no carbon emissions during production. Renewable energy sources such as solar energy, wind energy, and biomass are used for the production of green hydrogen.
Four main energy sources play a role in the production of green hydrogen
1. Heat Energy :It can be obtained from fossil fuels or renewable energy sources.
2. Electrical Energy: It is used in the electrolysis process by providing it from sources such as solar panels and wind turbines.
3. Photon Energy : It is used in the production of hydrogen directly from sunlight.
4. Biochemical Energy : Organic substances are enabled to produce hydrogen through natural processes.
Hydrogen Production from Solar Energy
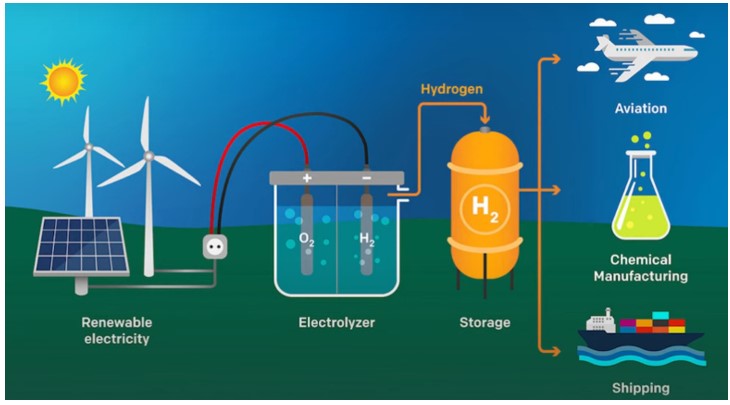
There are four basic methods for producing hydrogen using solar energy: photovoltaic, thermal energy, photo-electrolysis and bio-photolysis. Solar energy can be used in the production of hydrogen by converting it into electricity or heat through various systems. Photovoltaic (PV) systems produce hydrogen by electrolysis of water by converting sunlight directly into electricity.
Solar collectors and concentrated solar energy (CSP) systems, on the other hand, help to obtain hydrogen through thermochemical processes by producing high temperatures. The photo-electrolysis method allows water to decompose into hydrogen and oxygen using sunlight directly, while in the bio-photolysis process, some microorganisms produce hydrogen naturally using sunlight.