- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Trigeneration (Electricity-Heat-Hydrogen)
Trigeneration is an energy technology that enables the production of electricity, heat and cooling within the same system. While conventional cogeneration systems only generate electricity and heat, trigeneration systems can additionally produce cooling or hydrogen.
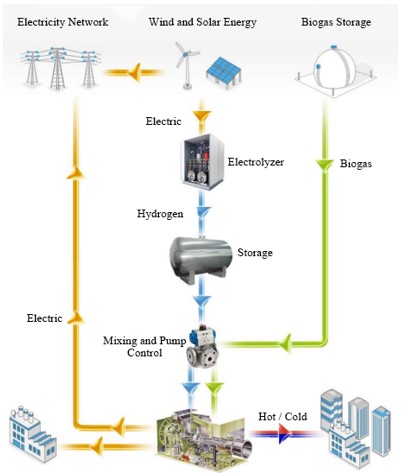
Trigeneration systems based on renewable energy sources offer great advantages in terms of sustainable energy production. For example:
- Electricity generation: The system can generate electricity through generators using hydrogen or natural gas as fuel.
- Heat recovery: The waste heat generated during production can be used to heat buildings or industrial plants.
- Hydrogen production: Excess energy can be used to produce hydrogen by electrolysis of water. This hydrogen can be stored and used as fuel.
Trigeneration technology, which is widely used especially in large facilities, hospitals and industrial enterprises, plays an important role in creating a more sustainable energy infrastructure in the future.s