- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Storage of Hydrogen
Efficient storage of hydrogen is of great importance for sustainable energy systems. Since hydrogen gas is very light and low density, special techniques have been developed to store a sufficient amount of energy. Hydrogen is usually stored in three different ways:
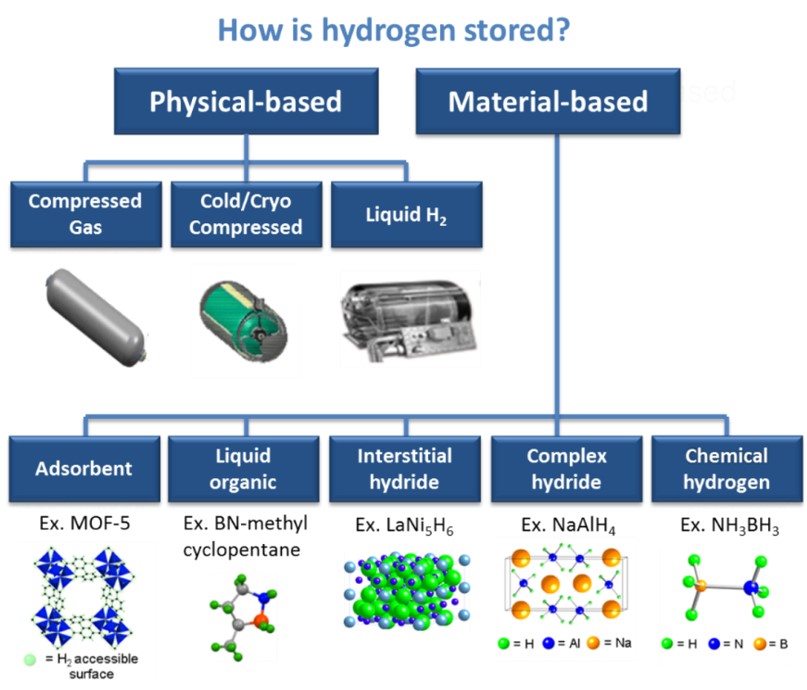
Storage as Gas
Hydrogen can be stored in high-pressure cylinders. Metal tanks or durable glass fiber-wrapped tanks ensure the safe transport of hydrogen.
Storage as Liquid
Hydrogen is cooled down to -253°C to make it liquid. This method allows more hydrogen to be stored in less volume, but requires extra energy to maintain low temperatures.
Chemical Storage
It can be stored by binding with chemical compounds such as hydrogen, ammonia or boron hydride. When necessary, hydrogen gas is obtained again by separating from these compounds.