- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Point Concentrators
Parabolic Dish Systems
These systems consist of reflectors in the shape of a dish that follow the sun throughout the day and concentrate the rays at the focal point. The sun's rays are directed to the focal point with the help of computer-controlled mirrors called heliostats. The liquid in the absorbent pipe here heats up to 600-700°C. This heat is converted into electrical energy by steam turbines.

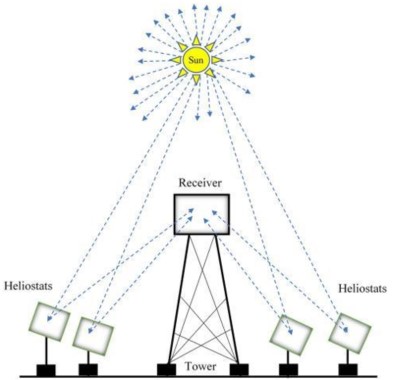
Central Receiver Systems
Central receiver systems have a tower-type structure. The system is based on large mirrors (heliostats) directed at the tower. These computer-controlled mirrors continuously reflect the sun's rays to the receiver at the top of the tower. The heat transfer fluids, such as molten salt, in the receiver reach temperatures of 350-600°C. This heat energy is used to generate electricity with the help of steam turbines.