- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Biogas Production
- Animal manure (cattle, sheep, poultry)
- Plant production waste
- Forest and paper industry waste
- Textile industry waste
- Sewage waste
- Food industry waste (milk, yeast, chocolate, beverage production, etc.)
- Agricultural industrial waste (oil, sugar factories, etc.)
- City solid waste



Biogas is a flammable gas mixture obtained by decomposing organic wastes by microorganisms in an oxygen-free environment. In the process:
Methane (CH₄): It is the most important component of biogas and constitutes its energy source
Carbon dioxide (CO₂): It is a natural by-product of the process.
Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) and nitrogen (N₂): May be present in small amounts depending on the type of waste.
The methane content determines the energy value of biogas. However, methane cannot be liquefied at low pressures like LPG; It needs a pressure of 280-350 bar to liquefy.
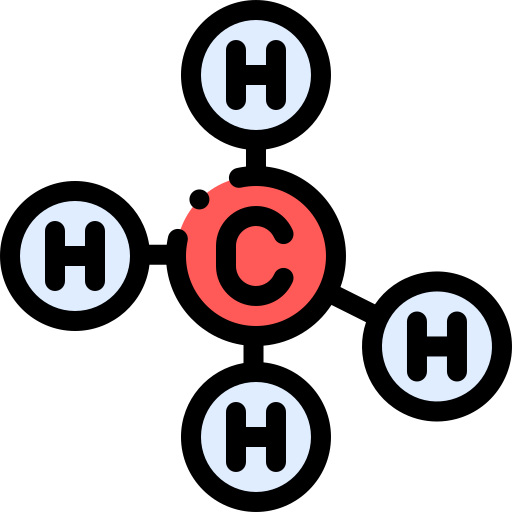
Biogas production depends on the chemical and physical properties of the wastes used . Important factors include:
- Type and composition of waste (animal, vegetable, domestic, etc.)
- The amount of foreign matter (soil, stone, metal, etc.)
- Particle size (smaller pieces ferment faster)
- Moisture content and organic matter content
- Generator (reactor) design (volume, insulation, mixing and heating systems)
- Fermentation temperature and pH balance

