- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
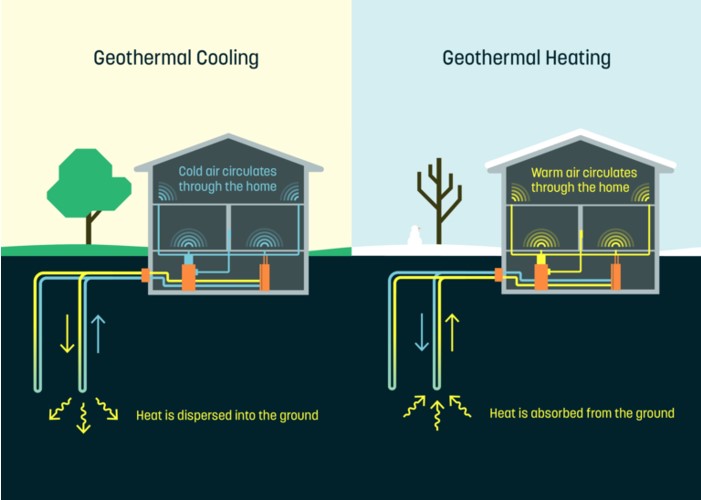
Residential Heating (Central Heating System)
Geothermal energy is a widely used energy source for heating homes. Depending on economic conditions, geothermal fluid is transported to buildings via central heating systems. When transported using specially insulated pipes, the temperature loss is quite low (approximately 0.1–0.3 °C/km). In central heating systems where geothermal fluid is used, hot water or steam drawn from wells is transmitted to the heating center via the main line. Here, the heat of the geothermal fluid is transferred to the circulation water circulating in the buildings by means of heat exchangers. The geothermal fluid, whose heat is taken, is reinjected back into the underground, ensuring sustainable use.