- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
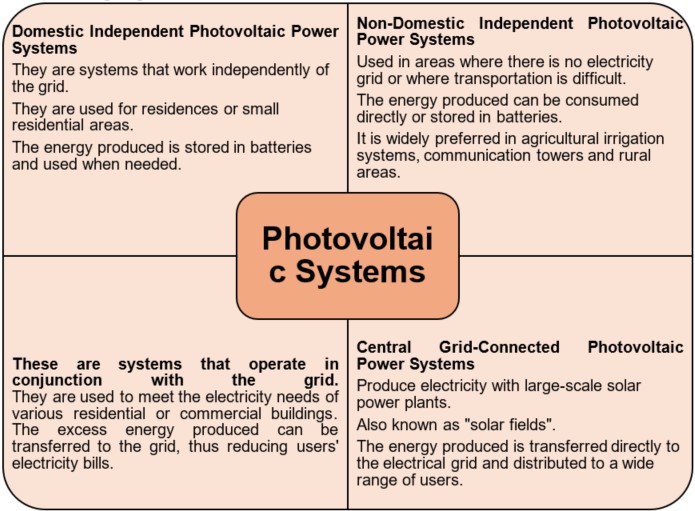
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
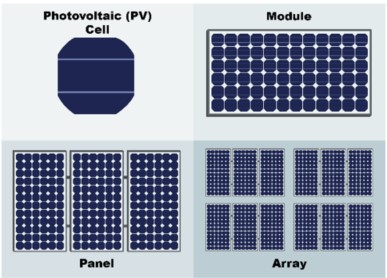
Systems that produce electricity directly from solar energy are called photovoltaic (PV) systems. The basic building blocks of these systems are photovoltaic cells (PV cells). When sunlight hits the surface of PV cells, electric current is produced. However, a single cell can produce a very low amount of direct current (DC). For higher electricity production, these cells are connected in series or parallel to form PV panels.
The most important advantages of photovoltaic systems are:
- They are durable and require little maintenance because they have no mechanical moving parts.
- They operate silently and do not emit harmful gases into the environment.
- They have a long service life.
- They can be designed in different powers from small microwatt levels to megawatt levels.
However, a large area is needed to install a high-efficiency system. The International Energy Agency Photovoltaic Power Systems Program (IEA-PVPS) has divided photovoltaic systems into four main groups: