- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
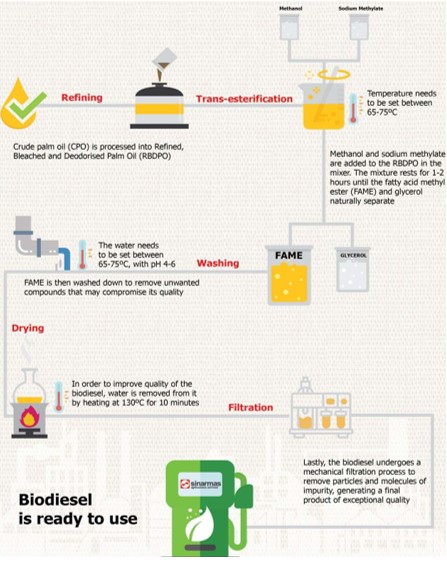
Biodiesel production
One of the main problems in the production of biodiesel is the high viscosity of the oils used. Therefore, the viscosity needs to be reduced before it can be used as a motor fuel. To achieve this, thermal and chemical treatments are applied to the oils. In heat treatment, which is the simplest method, oils are heated before they are introduced into the fuel system to reduce their viscosity. However, this method can lead to various problems, especially when used on mobile devices.
Chemical treatments are commonly preferred to reduce viscosity. Among these, the most effective and common method is the transesterification method. In this process, vegetable or animal fats are reacted with an alcohol to obtain biodiesel and glycerin as a by-product. In simpler terms, large-molecule oils react with small-molecule alcohols to turn into a more fluid liquid that can be used as motor fuel.
There are different alcohol and catalyst options in the transesterification reaction. Methanol and ethanol are the most commonly used alcohols. Acidic, basic or enzymatic catalysts can be preferred as catalysts. However, basic catalysts are usually more advantageous because:
It provides higher yields.
It is less corrosive.
The reaction time is shorter.
Acidic catalysts increase the cost of production because they require special acid-resistant tanks.