- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
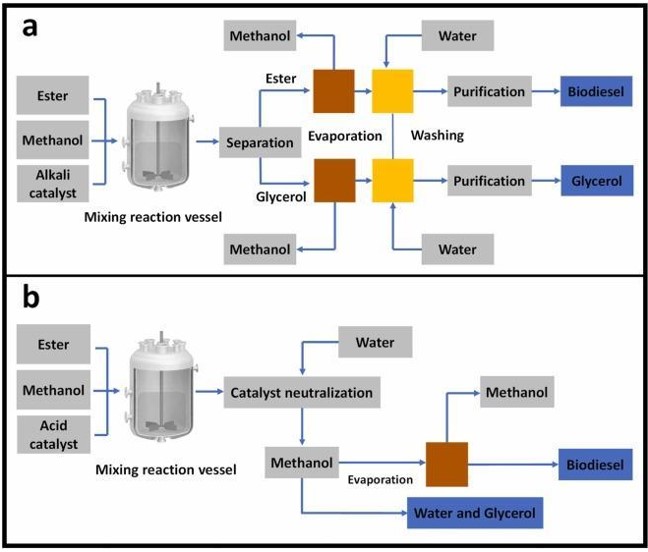
Basic Catalyst Biodiesel Production Stages
Mixing Catalyst and Alcohol
Usually, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH) is used as a catalyst. The catalyst is dissolved in alcohol with the help of a mixer and made ready for the reaction.
Reaction
The prepared catalyst-alcohol mixture is taken into the reactor with oil, which is the raw material of biodiesel. The reactor is kept closed to prevent alcohol loss. The reaction temperature is kept slightly above the boiling point of the alcohol (about 70°C) and the processing time can vary between 1 and 8 hours.
Separation
As a result of the reaction, two main products are formed: biodiesel and glycerin. Since glycerin is denser than biodiesel, it can be separated by the action of gravity. Centrifuges can be used in some plants to provide faster separation.
Removal of Alcohol
After the separation of glycerin and biodiesel, the remaining alcohol is removed by evaporation (flash evaporation) or distillation. In some systems, after this stage, the mixture is neutralized and the end products are treated before separation.
Neutralization of Glycerin
It contains glycerin, which is a by-product, unused catalyst and soap. These components are neutralized with an acid and stored as crude glycerin. With the purification process, glycerin with a purity of 80-88% can be obtained and presented to the industry. Glycerin with a purity of 99% can be produced by applying special processes.
Washing and Storage of Biodiesel
The biodiesel, separated from the glycerin, is washed with warm water and dried to remove the catalyst and soaps remaining in it. The final product is a liquid with a bright amber color and a viscosity close to that of diesel fuel.