- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Electricity Generation Methods
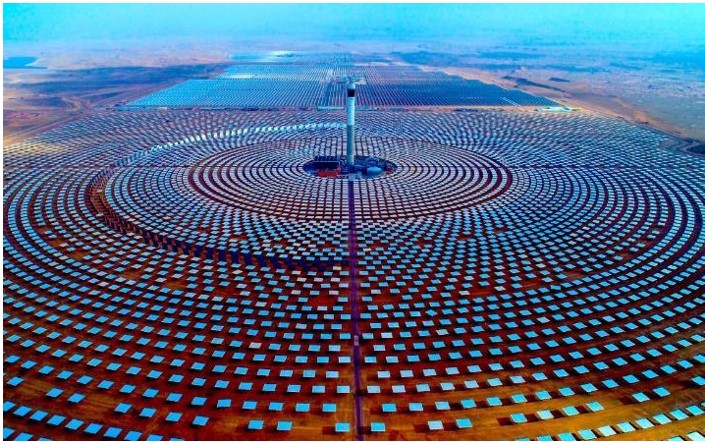

One of the commonly used methods for generating electricity from solar energy is Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems. These systems include parabolic, tower, and dish systems. The use of solar collectors is particularly widespread in countries close to the equator. Countries such as the United States, Japan, France, Italy, Greece, and Israel actively utilize these systems. Even in countries like Sweden, where sunny days are limited, solar collectors are used to produce hot water.
Solar Furnaces
Solar furnaces are devices that collect sunlight using parabolic-shaped structures, converting it into heat. These systems are commonly used for cooking and water heating purposes. Solar furnaces are especially popular in countries such as Pakistan, India, China, and Kenya.

Solar Collectors
Solar collectors, also known as "collectors," are systems that are classified into three groups based on their structural features:
- Flat-plate solar collectors: These are the most common type of solar collectors, consisting of a flat absorber plate that absorbs sunlight and converts it into heat.
- Vacuum tube (tubular) solar collectors: These collectors use vacuum tubes to minimize heat loss, improving efficiency, especially in colder climates.
- Non-glass solar collectors: These systems do not use glass as a covering material but instead use other materials to capture solar energy.
These collectors are designed based on the circulation of water and can be produced as either naturally or pump-assisted circulating, and can have either open or closed-loop systems.
Flat Collectors
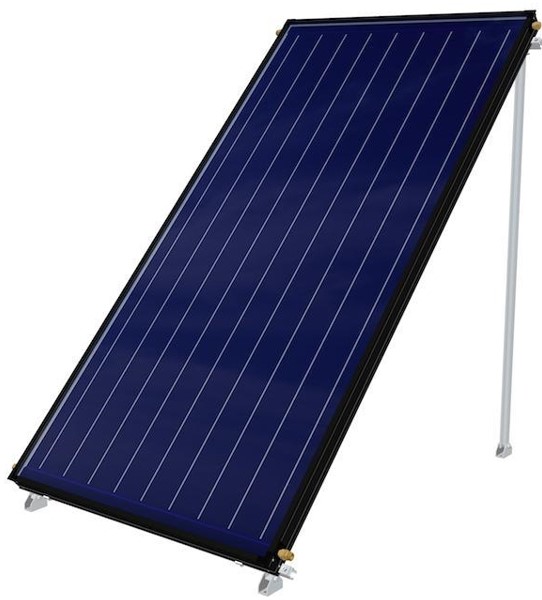

Flat collectors collect solar energy and transfer it to a fluid as heat. The fluid can be water, air or a different fluid. Air collectors lose more heat than liquid collectors. Therefore, they are used in heating residential and commercial buildings and drying processes. Liquid collectors are preferred in heating large buildings, industrial heating processes and cooling of buildings.
The structure of a flat-surface collector consists of three parts:
- An absorber plate with high absorption capacity
- Glass or plastic cover placed in front of the absorber plate These collectors use vacuum tubes to minimize heat loss, improving efficiency, especially in colder climates.
- Collector case made of metal, impregnated wood or plastic
Vacuum Tube Collectors
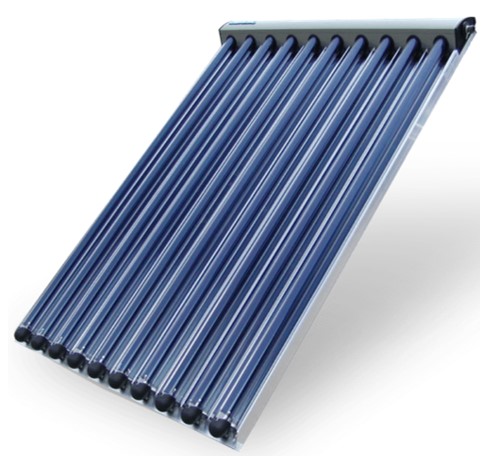

Vacuum tube collectors are systems designed using vacuum glass tubes. They have two intertwined tube structures and the air between the tubes is removed to create a vacuum environment. In this way, heat losses are minimized and energy efficiency is increased. The tubes are coated with a special surface to better absorb the sun's rays and convert them into heat. Thanks to their round structure, the sun's rays always come to the surface at a right angle, which provides more energy production compared to flat collectors.
Solar Pools
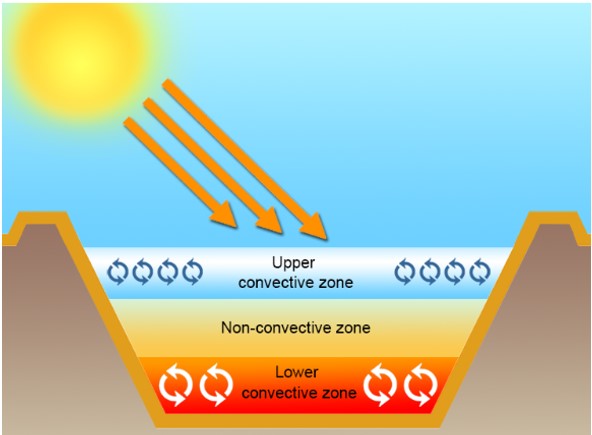
Solar pools are systems that collect and store solar energy as heat. The bottom of these pools, which are usually 5-6 meters deep, is made black to better absorb the sun's rays. The water temperature in solar pools can reach up to 90°C. There are layers with different salt ratios in the pool. While the water is colder in the upper parts due to the low salt ratio, the water remains warmer in the lower parts due to the higher salt ratio. The hot water in the lower part can be used for direct heating purposes or can be used for electricity generation. The efficiency of solar pools is approximately 20%. These systems are widely used especially in countries such as Israel, the USA and Australia. For example, there are solar pools with a capacity of 150 kW and 5 MW in Israel, 400 kW in the USA and 15 kW in Australia.
Glassless Solar Collectors
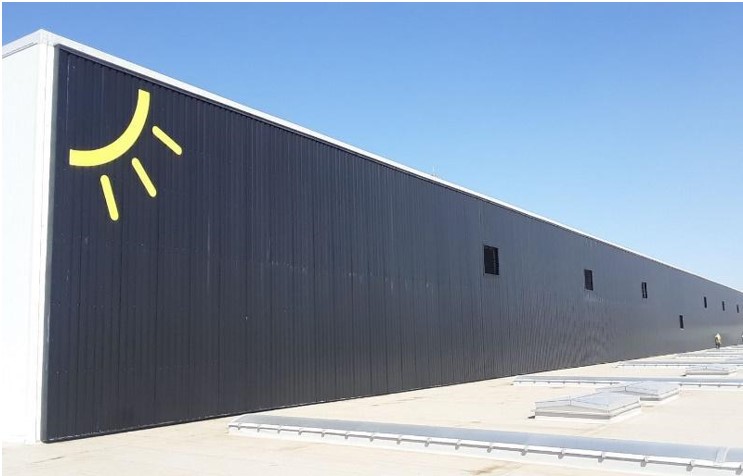

Glassless solar air collectors are solar air heating systems with a metal absorber surface that does not have a glass or similar cover on it. The most commonly used type of these systems, also known as SolarWall, is the "Air-Leaked Solar Collector" application. These collectors are used in commercial buildings, industry, agriculture and livestock sectors, and also in industrial processes to heat the outside air needed.
They are usually mounted on the exterior walls of buildings in order to better capture the low sun angle in the winter months and to benefit from the sun rays reflected from the snow surface.
Solar Water Distillation Systems
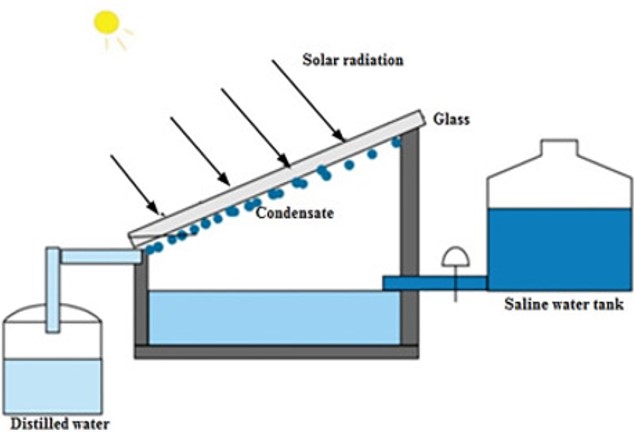
Obtaining drinking water using solar energy is an environmentally friendly and economical method. Especially in coastal areas where sunlight is intense, seawater purification can be carried out easily and efficiently. Two basic methods are used to convert seawater into drinking water. In the first method, evaporation, freezing, crystallization and filtration are applied for salt separation. In the second method, electrodialysis, extraction, ion exchange and diffusion techniques are used. The simplest water distillation system is the greenhouse type distillation system. In this system, the bottom of the distiller is designed in black to better absorb sunlight. The upper part is arranged in an airtight manner and inclined to the channel where fresh water will be collected. The sunlight passing through the glass surface heats the water in the distiller and causes it to evaporate. The rising water vapor condenses on the glass surface and turns into water droplets and slides down the inclined surface and accumulates in the collection container. The hotter the water, the higher the distillation efficiency. When the outside temperature drops, the condensation process accelerates, producing more fresh water
Vacuum Tube Collectors
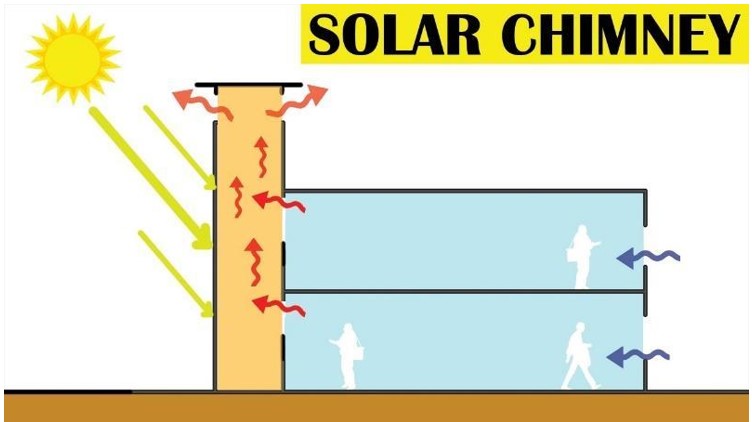
Solar chimney systems create air currents using solar energy and convert this movement into electrical energy. A large structure covered with transparent surfaces absorbs the sun's rays and heats the air inside more than the outside temperature. The heated air rises through a sloping roof and is directed to the chimney. The hot air reaching the chimney moves at a speed of approximately 15 m/s and rotates the wind turbine placed there, generating electricity.