- Definition and Types of Energy
- Myths And Misconceptions About Energy
- The Relationship Between Energy and Environment
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
- Greenhouse Gas Effect
- The Role of Human-Induced Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Renewable Energy Sources and Future Perspectives (video)
- Play and Learn
- Solar Energy Conversions
- Solar Energy Worldwide
- Solar Energy in Partner Countries
- Positive and Negative Impacts
- Technologies for Harnessing Solar Energy
- Solar thermal energy technologies and applications
- Electricity Generation Methods
- Passive Heating and Cooling of Residences with the Sun
- Concentrator solar power (CSP) systems and electricity generation
- Systems and Applications That Generate Electricity directly from solar rays
- Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
- Domestic PV Systems
- Off-Grid PV Systems
- Hybrid Connected Systems
- Materials Used in PV Cells
- Play and Learn
Renewable Energy Use in Global
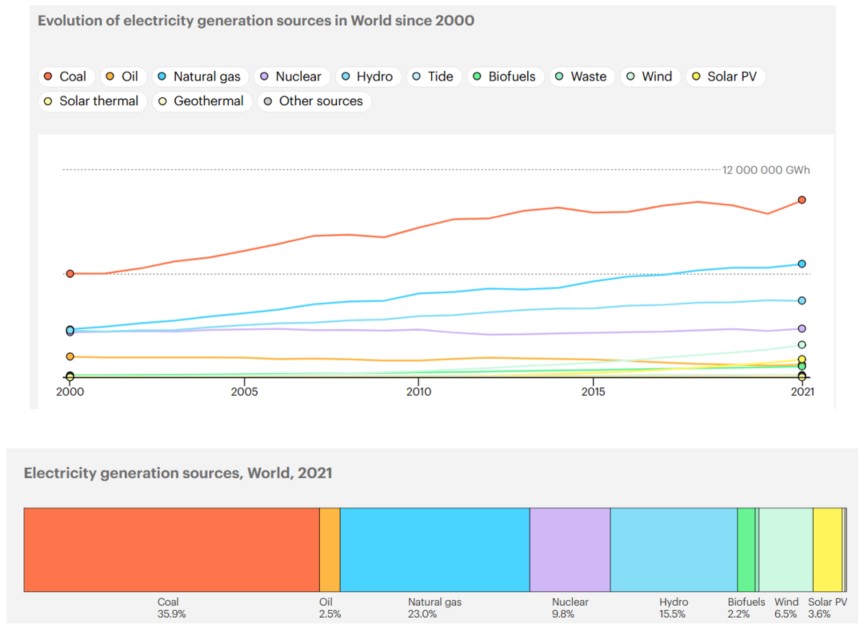
Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, remain the largest source of energy in the world, supplying about 80% of all the energy we use Ref . Renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, hydropower, and biomass, have grown rapidly in recent years and now contribute around 20% of global energy consumption Ref . Nuclear energy plays a smaller role, accounting for about 2.6% of the world's energy needs Ref .
When it comes to producing electricity, renewable energy has made significant progress. In 2023, renewable sources generated over 30% of the world's electricity, marking a steady shift towards cleaner energy Ref . Hydropower leads the way as the most widely used renewable electricity source, followed by wind and solar power, both of which have grown quickly thanks to advancements in technology. For example, solar energy production increased by nearly 25% in just one year Ref .
Despite these gains, fossil fuels still produce the majority of the world's electricity—about 57% in 2023. This reliance on fossil fuels continues to contribute to high levels of greenhouse gas emissions, which reached record highs in 2023, surpassing 40 billion metric tons Ref .
The shift towards renewable energy is critical for a sustainable future. Cleaner energy sources reduce pollution, combat climate change, and ensure we have reliable energy for generations to come. However, this transition requires significant investment and global cooperation. While challenges remain, such as the need for better energy storage and more efficient technology, the progress made so far shows that renewable energy can play a key role in shaping a healthier planet.
Renewable energy sources have experienced rapid growth worldwide in recent years. The share of renewable energy in global energy consumption is increasing, and investments in these resources are growing rapidly. Total renewable electricity generation reached an all-time high in 2022, surpassing 8,500 TWh, which is more than 600 TWh (approximately 8%) higher than in 2021. This increase was primarily due to the growth in wind and solar PV production, both of which grew by approximately 270 TWh. Although hydroelectric power, the world's largest renewable electricity source, still saw a 70 TWh increase despite drought conditions affecting hydroelectric production in many regions including China, Europe, and the United States, the global share of renewable energy in electricity production rose to about 30%, up 1.5 percentage points from 2021. As of 2022, renewable energy sources account for approximately 30% of global energy production. Notably, investments in solar and wind energy have been at the forefront of this growth.